A Guide to Die Cutting vs. Laser Cutting vs. Digital Cutting

ESPE Manufacturing Co., Inc. is a fabrication company specializing in the production of electrical insulation materials and custom plastic components. Using advanced industrial die cutting and fabrication techniques, we manufacture washers, gaskets, bushings, and other high-quality parts from a wide range of non-metal materials. Our manufacturing capabilities also include electrical insulation parts and barriers that are designed and manufactured in compliance with strict quality and safety standards.
The Methods of Die Cutting at ESPE
Our die cutting services allow for the quick and efficient production of precise, uniform parts from various materials. To meet a range of customer specifications, we offer the following techniques:
Flatbed or Steel Rule
Flatbed die cutting, also referred to as steel rule die cutting, is a technique that involves cutting or perforating a custom shape from a workpiece using a flatbed press and steel rule. This type of die cutting is well-suited for handling thick materials, fabricating relatively large parts, and processing low-volume production runs. Compatible materials include everything from fabric, paper, plastic, and rubber to a variety of composites and laminates.
Punch Press
Punch press die cutting cuts or shapes parts from thin materials using a die set consisting of male and female dies. Placed on opposite sides of the workpiece, the two dies punch a hole through the material when mated. Punch pressing is ideal for producing hole-intensive parts, however, it is important to keep in mind that this process can generate a great deal of noise and is limited to materials with thicknesses under ¼ inch.
With customizable dies and various material options, die cutting can be used to create parts for a wide range of applications. A few of the most common materials used to produce custom die-cut electrical insulation parts include:
- Fishpaper. Lightweight and easy to manipulate, electrical-grade fishpaper is commonly used to fabricate high-strength insulating washers, gaskets, bushings, and other products that can withstand harsh environments.
- ITW Formex®. With its superior dielectric strength and flame-retardant properties, Formex® is a great option for electrical insulation barriers.
- Vulcanized fibre. Vulcanized fibre is an impact- and abrasion-resistant material that is well-suited for washers, switch and appliance insulation, gaskets, and automobile parts.
- Nomex®. The unique heat-resistant synthetic fibers of Nomex® make it an excellent choice for the fabrication of chemical-, thermal-, and radiation-resistant parts used in aerospace, automotive, and electrical power applications.
- Insulating polymers. Nylon, Teflon, Polycarbonate, PVC, and other electrically- or thermally-insulating polymers can be used to fabricate protective electrical elements such as electric cables, switch boxes, gears, seals, and bearings.
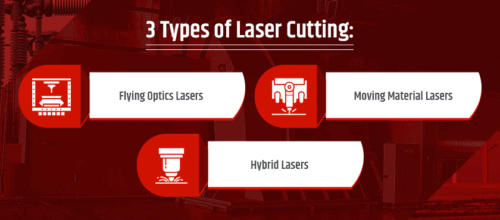
What are Different Types of Laser Cutting?
Our laser cutting services include the following techniques:
- Flying optics lasers. The flying optics laser cutting process involves holding the workpiece in place while a laser follows a computer-programmed path to make cuts along X and Y axes. The process is extremely fast and precise, making it ideal for projects requiring tight tolerances and quick turnaround times.
- Moving material lasers. With moving material lasers, the workpiece moves along X and Y axes while a stationary laser beam performs the desired cuts. This type of laser cutting requires fewer optics than the other techniques and creates a consistent standoff distance between the beam source and workpiece.
- Hybrid lasers. Combining the advantages of flying optics and moving material laser cutting, hybrid laser cutting involves moving a laser along the Y-axis while the workpiece moves along the X-axis. With this technique, a much more consistent beam delivery can be achieved, resulting in lower power consumption during the cutting process.
Laser cutting offers several advantages over other cutting methods, including superior precision, flexibility, speed, and cost-effectiveness. This makes it a preferred fabrication choice across a wide range of industries, including:
- Automotive. The speed, accuracy, and repeatability of laser cutting make it well-suited for fabricating instrument panels, electronic components, interior covers, and other automotive products that require a high level of consistency and uniformity.
- Die, mold, and tool industries. Lasers can make cuts at various depths with exceptional accuracy, making laser cutting perfect for creating extremely accurate dies and high-precision injection molds. In the tool industry, laser cutting is used to fabricate simple hand tools and engrave logo designs on rubber tool handles.
- Medical devices. Laser cutting is commonly used to manufacture small, high-precision parts that are incorporated into sophisticated medical devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic tools.
Digital Cutting
Unlike conventional die cutting techniques, digital cutting makes precision cuts without the use of a die. This technique offers many of the same advantages as conventional die cutting, using bits, lasers, and small blades to make precise cuts, scores, and creases. Benefits of digital cutting include:
- Quicker turnaround. Digital cutting enables faster production and shorter lead times since it eliminates the need to switch out die shapes.
- Enhanced precision. The digitally controlled blades, lasers, and bits used to perform the cuts enable a higher level of precision.
- Reduced costs. By eliminating the costs associated with manufacturing and using dies, digital cutting can be performed at a lower cost than conventional die cutting.
- Software integration. Digital cutting is compatible with a wide range of software programs, and the integration process is relatively quick and straightforward. ESPE Manufacturing will machine directly from a range of file types so the shape you send is the part you receive.
How Do They Compare?
Die Cutting vs. Laser Cutting
When deciding between die and laser cutting, it is important to consider the benefits and limitations of each method as it relates to your project’s needs. Some factors to consider include:
- Cost and efficiency. Die cutting requires separate dies to perform each different type of cut, which can become expensive and time-consuming. An advantage of laser cutting is that the machine can be programmed to cut virtually any size or design without having to manufacture or change out dies. This makes it a cheaper and more cost-effective option for prototyping and small-scale production runs. For higher-volume production runs, however, die cutting can typically process materials at a faster rate and lower cost.
- Material compatibility. While laser cutting is compatible with a wider range of materials, die cutting tends to be better suited for difficult-to-cut materials.
- Design complexity. While die cutting is great for creating straightforward designs at high speeds, laser cutting is better suited for achieving more intricate or difficult patterns and details.
Die Cutting vs. Digital Cutting
Factors to consider when deciding between die cutting and digital cutting include:
- Cost and efficiency.While tooling costs are more expensive with die cutting, using the die across a large volume of items helps offset this added expense. For this reason, die cutting tends to be more time- and cost-efficient for high-volume production runs, while digital cutting is better suited for low- to medium-volume runs.
- Material compatibility. Digital cutting is generally preferred for processing thicker, tougher materials, while die cutting is better suited for thinner materials.
- Design complexity. When it comes to making highly intricate or detailed cuts, digital cutting tends to outperform die cutting. However, die cutting is the preferred method for rapidly and efficiently punching out a large volume of identical forms.
Partner with ESPE Manufacturing!
With a wide range of material options and cutting techniques available, ESPE offers customers the design flexibility to create custom parts in the most cost- and time-effective way possible. We can perform simple or complex cuts on a range of plastics, electrical insulators, and other non-metallic materials, producing high-quality products that conform to exact technical specifications and strict industry standards. Several decades of experience in our field allows us to provide personalized guidance and innovative solutions for the most complex design challenges.
To learn more about our capabilities, please view our services page, contact us, or request a quote today.